Curriculum, Extra-Curricular Opportunities and Educational Trips
| Year Group | Course |
| 1 | Clock & Sports Emblems Projects |
| 2 | Wooden CAM Toy & F1 in Schools Entry Level |
| 3 | Architectural Project |
| 4 | D&T GCSE Level |
| 5 | D&T GCSE Level |
| 6 | D&T AS Level |
| 7 | D&T A Level |
GCSE
The GCSE Design and Technology (DT) curriculum by Pearson (Edexcel) is designed to give students a broad and balanced understanding of the subject by combining creative design processes with technical and theoretical knowledge. The curriculum emphasizes the design process, the use of materials, and the application of new and emerging technologies.
Here’s an outline of the Pearson Edexcel GCSE Design and Technology curriculum:
1. Core Content Areas
The GCSE Design and Technology curriculum is divided into two major sections: core content that applies to all students, and a material category that students can specialize in.
1.1 Core Technical Principles
Students will develop knowledge and understanding of:
- New and Emerging Technologies: Impact of new technologies on production, society, and the environment.
- Energy Generation and Storage: How energy is produced and stored, and its influence on design choices.
- Developments in Modern and Smart Materials: Understanding materials like smart materials, composites, and nanomaterials.
- Systems Approach to Designing: Introduction to systems, inputs, processes, and outputs.
- Mechanical Devices: Movement principles, forces, and mechanisms like levers, cams, and gears.
- Materials and their Properties: Overview of a wide range of materials, including wood, metal, plastics, and textiles, and their properties.
- Investigation and Research: Understanding user needs, market research, design problems, and developing design briefs.
- Design Strategies: Techniques such as iterative design, user-centered design, and the role of collaboration and feedback.
- Prototype Development: Sketching, modelling, using CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and testing to refine ideas.
- Tools, Equipment, and Processes: Knowledge of tools and processes related to their chosen material focus, including safety.
- Design Communication: Techniques to present ideas effectively, such as technical drawing and digital media.
- Evaluating Designs: Iterative evaluation throughout the design process, reflecting on strengths, weaknesses, and ethical/sustainability considerations.
Students will focus on one area for more in-depth study: Polymers
For Polymers students will learn:
- Material Properties: Key physical and working properties of the chosen material group.
- Processes and Techniques: Practical skills for working with the materials, including cutting, shaping, joining, and finishing.
- Industrial Processes: Understanding of large-scale production methods, environmental impacts, and sustainability of materials.
3. Assessment Overview
The GCSE Design and Technology assessment consists of two main components:
3.1 Component 1: Examination (50%)
Written Paper (1 hour 45 minutes):
Covers core technical principles, designing and making principles, and specialist material knowledge.
Sections include both short-answer and extended-response questions, focusing on both general and in-depth knowledge.
3.2 Component 2: Non-Exam Assessment (NEA) (50%)
Design and Make Project:
Students undertake a substantial design and make project based on a context set by Pearson. They are required to investigate, design, develop, and create a prototype product.
The project is evaluated based on:
- Identifying and investigating design possibilities.
- Producing a design brief and specification.
- Generating and developing design ideas.
- Making a prototype.
- Evaluating the prototype.
4. Key Skills Developed
- Creative Thinking and Innovation: Encouraging students to explore a range of design possibilities and think critically about the impact of their designs.
- Practical and Technical Competency: Gaining hands-on skills in working with various materials and processes.
- Problem Solving: Developing the ability to analyze problems and generate solutions through design thinking.
- Sustainability and Ethical Awareness: Understanding the environmental and social impact of design choices.
- Technological Literacy: Using digital tools, including CAD/CAM, to create and test design ideas.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: A strong focus is placed on sustainable design and consideration of environmental effects.
- User-Centered Design The curriculum emphasizes understanding user needs and creating designs that are functional and accessible.
- Emerging Technologies: Students are introduced to new materials and production techniques, such as 3D printing and smart technologies, to prepare them for future developments in the field. The Pearson Edexcel GCSE Design and Technology course offers students a broad foundation in both design thinking and technical skills, preparing them for further education or careers in design, engineering, architecture, and manufacturing.
AS Level, starting 2024-2025
The Cambridge International AS Level Design and Technology course aims to:
- Encourage creativity, innovation, and the application of design principles in developing functional and aesthetic products.
- Develop technical and practical skills in a range of design and technology disciplines, including materials, systems, and processes.
- Promote awareness of contemporary technologies and their environmental, social, and economic impacts.
- Foster problem-solving skills by applying design thinking and iterative processes to address real-world challenges.
- Prepare students for further education or careers in fields such as design, engineering, architecture, and manufacturing.
2. Key Content Areas
Candidates for Cambridge International AS Level study Topics 1–12.1 The design process
2 Design principles
3 Communication
4 Design and technology in society
5 Sustainable design
6 Health and safety
7 Aesthetics and ergonomics
8 Materials and components
9 Stages in materials processing
10 Materials processing
11 Energy and control systems
12 Technology
AS Level candidates also apply the AS Level content and skills in a practical context in the Component 2 coursework.
Candidates for Cambridge International A Level study the AS Level topics and the following topics:
13 Industrial practices
14 Business and commercial practices
15 Quantity production
16 Materials processing in industry
17 Quality systems
18 Digital technology.
A Level candidates also apply the AS and A Level content and skills in a practical context in Component 4 coursework.
3. Assessment Overview
The AS Level D&T course assessment consists of two main components, both focusing on theoretical knowledge and design skills: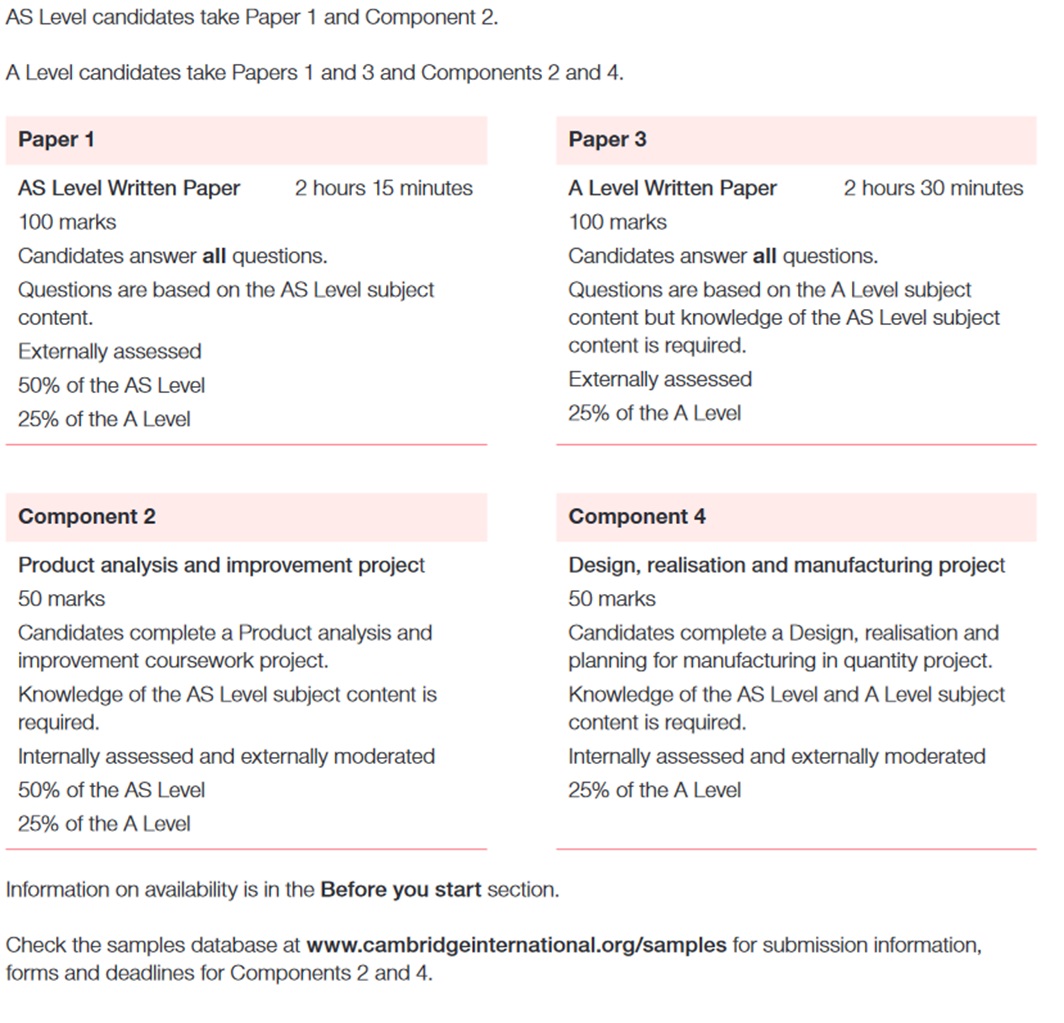
4. Learning Outcomes
By the end of the AS Level course, students will:- Demonstrate an understanding of the design process and its applications in developing products that meet user needs.
- Apply knowledge of materials and production techniques to create functional, sustainable, and innovative designs.
- Use effective research, analysis, and problem-solving techniques to address design challenges.
- Communicate ideas effectively through a range of methods, including sketches, technical drawings, and digital models.
- Understand the role of new technologies in design and manufacturing, and their implications for the environment and society.
- Develop practical skills in selecting and using materials, tools, and processes safely and efficiently.
5. Key Themes
Several key themes run throughout the AS Level D&T course:- Innovation and Creativity: Encouraging students to think outside the box and develop unique, practical solutions to design challenges.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Understanding the environmental and ethical implications of design choices, including material selection, production processes, and product lifecycle.
- User-Centered Design: Emphasizing the importance of understanding and meeting user needs through careful research and testing.
- Technology and Society: Investigating how modern technologies are shaping design, manufacturing, and consumption in today’s world, and exploring their future potential.
6. Skills Developed
The course is designed to develop a wide range of skills, including:- Critical thinking and analysis: Understanding complex design problems and evaluating potential solutions.
- Technical literacy: Gaining proficiency in technical knowledge related to materials, processes, and systems.
- Communication skills: Learning to express design ideas clearly and effectively through sketches, drawings, and digital tools.
- Practical skills: Developing hands-on experience with tools, materials, and production techniques.
- Research and investigation: Conducting market research, gathering user feedback, and refining design ideas based on evidence.
- Teamwork and collaboration: Working collaboratively to develop and present design solutions in a professional context.
This Cambridge AS Level course provides a strong foundation in both theoretical and practical aspects of design and technology, preparing students for further education in design-related fields or technical careers in engineering, manufacturing, or product development.
A level (2024-2025, Y7 only)
The Pearson Edexcel A Level Design and Technology (D&T) curriculum is designed to develop students' knowledge, understanding, and skills in product design and innovation. It emphasizes both the practical and theoretical aspects of design, preparing students for further education or careers in design, engineering, and other related fields. The course combines creativity, critical thinking, technical skills, and knowledge of new and emerging technologies.
1. Course Aims
The Pearson A Level Design and Technology curriculum aims to:- Encourage students to use creativity and imagination in designing and developing prototypes and products.
- Develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and practical skills.
- Equip students with knowledge of materials, manufacturing processes, and technologies, including digital and traditional methods.
- Prepare students for further study in design, engineering, or related fields, as well as for careers in design-based industries.
- Promote sustainability, ethical considerations, and the awareness of technological developments in design.
2. Key Content Areas
The A Level Design and Technology course focuses on both design and technical principles, offering a comprehensive understanding of the subject.2.1 Core Content Areas
The course covers a wide range of topics, divided into two key sections: Technical Principles and Designing and Making Principles.2.1.1 Technical Principles
Students will develop an understanding of:- Materials and their Applications: The properties, uses, and selection of materials (e.g., metals, plastics, textiles, woods, and composites).
- Performance Characteristics of Materials: The physical and mechanical properties of materials, including how they perform in different environments.
- Processes and Techniques: An understanding of how materials are processed and manufactured, including cutting, shaping, forming, joining, and finishing techniques.
- Digital Design and Manufacture: The role of CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and other digital tools in the design and manufacturing process.
- Product Development: How products are developed from concept to final production, focusing on iterative design and the use of prototypes.
- Modern Industrial and Commercial Practices: An overview of how products are made on a large scale in different industries, considering automation, lean manufacturing, and quality control.
- Sustainability and Environmental Issues: The impact of design and manufacturing processes on the environment, and the importance of designing sustainable, eco-friendly products.
- Health and Safety: The importance of health and safety in design and manufacturing, including risk assessments and safe working practices.
2.1.2 Designing and Making Principles
Students will explore:- Design Methods and Processes: How to approach design problems, generate ideas, and develop solutions through research, brainstorming, and iterative design.
- Design Theory and Movements: Key design movements, including modernism, postmodernism, and sustainable design.
- User-Centred Design: How to focus on the needs, wants, and limitations of the user, ensuring designs are functional and accessible.
- Innovation and Design for Manufacture: How to create innovative designs that can be efficiently manufactured, considering cost, materials, and processes.
- Product Analysis and Evaluation: Techniques for analyzing existing products and evaluating their effectiveness, usability, and marketability.
- Prototyping: The role of prototyping in testing and refining ideas, using tools such as 3D printing, laser cutting, and traditional workshop methods.
- Iterative Design Process: How to continuously develop and improve designs through evaluation and feedback.
3. Assessment Overview
The A Level Design and Technology assessment consists of both written examinations and a Non-Examined Assessment (NEA), which is a practical design project.3.1 Paper 1: Principles of Design and Technology (50%)
- Duration: 2 hours 30 minutes
- Content: This written exam covers both technical principles and designing and making principles.
- Section A: Mixture of short-answer, multiple-choice, and extended-response questions, focusing on technical principles such as materials, processes, and technologies.
- Section B: Longer questions based on design scenarios, case studies, and the analysis of design problems, requiring students to demonstrate their understanding of both technical and design principles.
3.2 Non-Examined Assessment (NEA): Independent Design and Make Project (50%)
- Content: The NEA is a substantial design-and-make project where students are required to:
- Identify a Problem or Opportunity: Based on real-world scenarios, students identify a design problem or opportunity that they will address through their project.
- Investigate and Research: Conduct thorough research, including user feedback, market analysis, and exploration of existing products.
- Develop Design Ideas: Generate, refine, and develop design ideas, considering user needs, material constraints, and sustainability.
- Make a Prototype: Create a fully functional prototype using appropriate materials, tools, and processes.
- Evaluate the Design: Test and evaluate the prototype based on feedback, and propose improvements for future iterations.
- Portfolio: Students submit a portfolio of evidence, typically 40–50 pages, documenting the design process from research to final evaluation.
4. Learning Outcomes
By the end of the A Level course, students should be able to:- Apply knowledge of materials, processes, and technologies to develop functional, innovative, and sustainable products.
- Generate and develop design ideas that address real-world problems and opportunities, using creative and analytical thinking.
- Understand the importance of user needs and design products that are accessible, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
- Use CAD/CAM and other modern technologies in the design and manufacturing process.
- Evaluate products critically, understanding the trade-offs between different materials, production methods, and user needs.
- Work independently on design projects, managing time, resources, and processes effectively.
5. Key Themes in the Curriculum
- Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility: A focus on creating products that minimize environmental impact, with an emphasis on sustainable materials, manufacturing processes, and product lifecycles.
- Innovation and Technology: Encouraging students to explore the role of emerging technologies (e.g., 3D printing, robotics, smart materials) in shaping future design and production.
- Ethical and Social Considerations: Addressing the ethical implications of design choices, including the social impact of products and the importance of responsible consumption.
- Real-World Problem Solving: Students engage with real-world problems, learning to balance aesthetics, functionality, cost, and sustainability in their designs.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Integrating concepts from science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) with design, art, and creativity.
6. Skills Developed
The Pearson Edexcel A Level Design and Technology curriculum develops a range of valuable skills:- Creative Thinking and Innovation: Students learn to think creatively and generate new ideas for products and systems.
- Technical Skills: Hands-on experience with tools, materials, and manufacturing processes.
- Problem Solving and Critical Thinking: Applying knowledge to solve design challenges, analyzing constraints, and making informed decisions.
- Project Management: Planning, organizing, and executing a complex design project over time.
- Communication: Effective communication of design ideas through sketches, technical drawings, and digital presentations.
- Collaboration: Working with others, including clients and users, to refine designs and receive feedback.
The Pearson Edexcel A Level Design and Technology curriculum provides students with a strong foundation in both the creative and technical aspects of design, preparing them for higher education or careers in design, engineering, architecture, product development, and related fields.
Extra-Curricular Opportunities and Educational Trips
- D&T Club
Students are able to explore different engineering and design challenges in a more relaxed setting.
Staff In-charge: OAN & STU
- F1 in Schools
Students follow a structured set of tutorials and workshops to guide them through material and requirements of the F1 in Schools in the hope to compete in the National Finals, hosted by the school.
Staff In-charge: MIH
Staff Involved: OAN, STU, KDE, ALS
- D&T Open Workshop
This is aimed at students who may need access to the workshop tools and equipment, and/or to review material with a specialist teacher a part of a support system.
Staff In-charge: OAN & STU
- On site visits to factories/workshops with small groups of students (years 6 & 7) where possible
